In simple words, we call the perimeter of any shape the total length of its outer edges. Whether you are fencing a garden, making a photo frame, planning to design a logo, measuring materials, or solving geometry problems – it is very important for you to calculate the perimeter accurately everywhere. Our Perimeter Calculator lets you quickly find the perimeter of common and complex shapes like square, rectangle, triangle, circle, semicircle, sector, ellipse, trapezoid, parallelogram, rhombus, kite, annulus (ring) and regular polygons. Just choose the shape, enter the dimensions, select the unit – you will get accurate results in a few seconds!
What is a Perimeter? (Simple and Clear Understanding)
The perimeter is the boundary or total length of all the sides/edges of any 2D shape – just like when you think about how much wire is needed before erecting a fence. It’s always measured in linear units, such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), inches (in), or feet (ft) – just like length, not square units!
For polygons (such as squares, rectangles, triangles), simply add up the lengths of all the sides – it’s a simple addition game.
For circles or curved shapes, it’s called the circumference – that’s the magic of a different formula!
Where does it come in handy in real life? I’ve seen it used in projects like: fencing, wiring, photo framing, road design, fabric cutting, landscaping, sports tracks – everywhere these calculations save time and money. Planning a garden boundary? This is the tool!
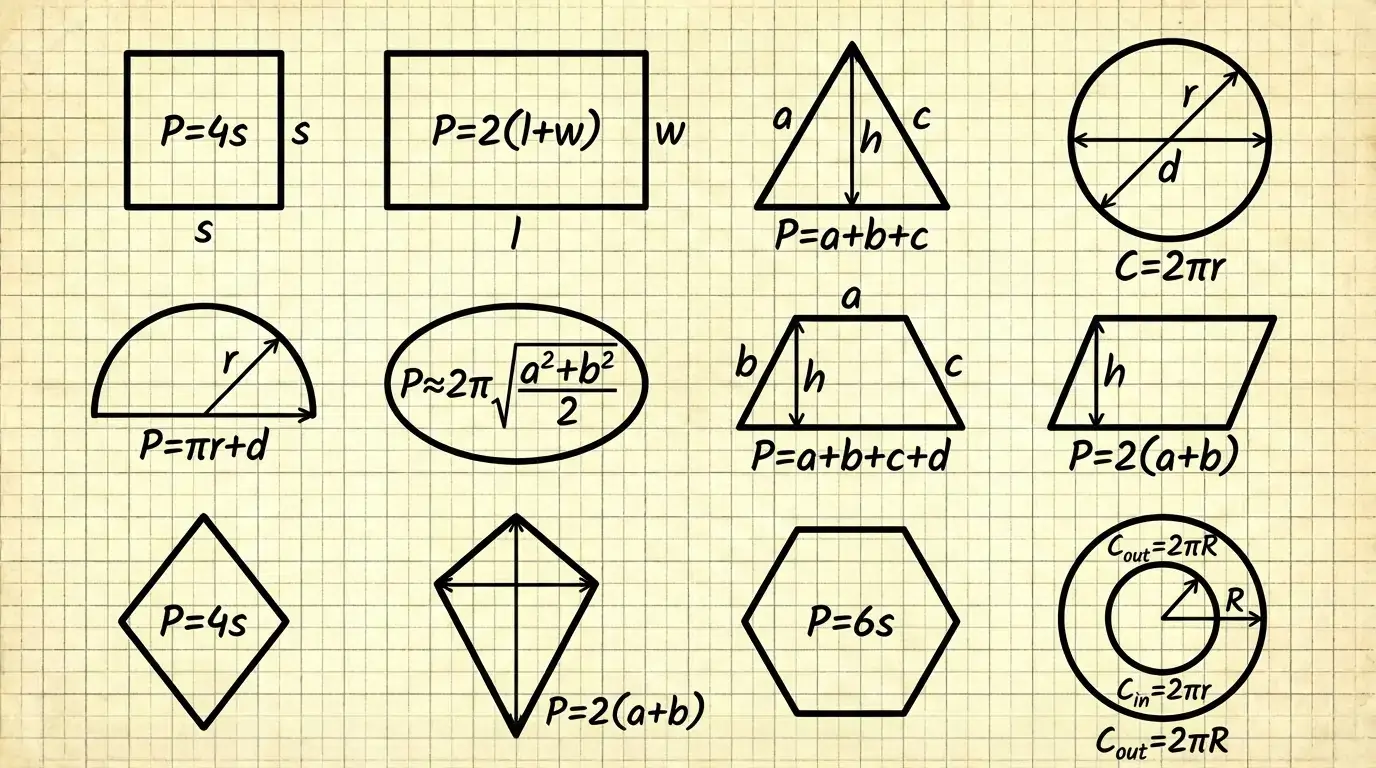
Perimeter Formulas at a Glance
| Shape | Perimeter Formula |
|---|---|
| Square | P = 4a |
| Rectangle | P = 2(a + b) |
| Triangle | P = a + b + c |
| Circle | P = 2πr or P = πd |
| Semicircle | P = πr + 2r |
| Circle Sector | P = r(θ + 2) (θ in radians) |
| Ellipse (approx.) | P ≈ π[3(a + b) − √((3a + b)(a + 3b))] |
| Trapezoid | P = a + b + c + d |
| Parallelogram | P = 2(a + b) |
| Rhombus | P = 4a |
| Kite | P = 2(a + b) |
| Annulus (Ring) | P = 2π(R + r) |
| Regular Polygon | P = n × a |
Where:
- a, b, c, d = side lengths
- r = radius
- d = diameter
- R = outer radius
- θ = angle in radians
- n = number of sides
How to Use the Perimeter Calculator
- Select the geometric shape from the dropdown menu
- Enter the required dimensions (side length, radius, angle, etc.)
- Choose your preferred unit of measurement
- Click Calculate to instantly get the perimeter
The calculator automatically applies the correct formula, handles curved edges, and provides accurate results with unit consistency.
Perimeter by Shape: Formula, Example, and Use Case
Square:
Formula:
P = 4a
Example:
If a square has a side length of 4 m:
P = 4 × 4 = 16 m
How to measure:
Measure one side only — all sides are equal.
Real-world use:
Framing square photos, tile layout, floor edging.
Rectangle:
Formula:
P = 2(a + b)
Example:
a = 5 m, b = 3 m
P = 2(5 + 3) = 16 m
How to measure:
Measure length and width; opposite sides are equal.
Real-world use:
Room borders, fencing rectangular plots.
Triangle:
Formula:
P = a + b + c
Example:
Sides: 3 m, 4 m, 5 m
P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 m
How to measure:
Measure all three sides. For unknown sides, use trigonometry or law of cosines.
Real-world use:
Roof trusses, triangular garden beds.
Circle (Circumference):
Formulas:
P = 2πr
P = πd
Example:
Radius r = 0.5 m
P = 2π × 0.5 ≈ 3.1416 m
How to measure:
Measure diameter across the center, or wrap a string around the circle.
Real-world use:
Wheels, circular tables, round tracks.
Semicircle:
Formula:
P = πr + 2r
Example:
r = 1 m
P = π × 1 + 2 × 1 ≈ 5.1416 m
How to measure:
Include both the curved arc and the straight diameter.
Real-world use:
Half-round patios, archways.
Circle Sector:
Formula:
P = r(θ + 2) (θ must be in radians)
Example:
r = 2 m, θ = π/3
P = 2(π/3 + 2) ≈ 5.094 m
How to measure:
Measure radius and central angle.
Real-world use:
Pizza slices, fan blades, curved flower beds.
Ellipse:
Approximate Formula:
P ≈ π[3(a + b) − √((3a + b)(a + 3b))]
Example:
a = 4 m, b = 2 m
P ≈ 19.38 m
How to measure:
Measure semi-major and semi-minor axes from the center.
Real-world use:
Athletic tracks, elliptical gardens.
Trapezoid:
Formula:
P = a + b + c + d
Example:
Sides: 3 m, 5 m, 4 m, 4 m
P = 16 m
How to measure:
Measure all four sides individually.
Real-world use:
Roof panels, landscaping sections.
Parallelogram:
Formula:
P = 2(a + b)
Example:
a = 4 m, b = 3 m
P = 2(4 + 3) = 14 m
How to measure:
Measure one base and one side.
Real-world use:
Fabric design, construction layouts.
Rhombus:
Formula:
P = 4a
Example:
a = 5 m
P = 20 m
How to measure:
Measure one side; all sides are equal.
Real-world use:
Decorative tiles, diamond shapes.
Kite:
Formula:
P = 2(a + b)
Example:
a = 3 m, b = 5 m
P = 2(3 + 5) = 16 m
How to measure:
Measure two adjacent unequal sides.
Real-world use:
Kite design, architectural patterns.
Annulus (Ring):
Formula:
P = 2π(R + r)
Example:
Outer radius R = 5 m, inner radius r = 3 m
P = 2π(8) ≈ 50.265 m
How to measure:
Measure both radii from the same center point.
Real-world use:
Washers, rings, circular paths.
Regular Polygon:
Formula:
P = n × a
Example:
Regular octagon (n = 8), side a = 1 m
P = 8 m
How to measure:
Measure one side and count the number of sides.
Real-world use:
Gazebos, tiles, paving stones.
Measurement Tips for Perimeter Calculations
- Always use consistent units
- For curved shapes, use flexible measuring tape or string
- Measure through the center for circular shapes
- Avoid rounding until the final step
- Double-check symmetry assumptions before using shortcut formulas
Reverse Formulas and Conversions
If you already know the perimeter and need another value:
These reverse formulas are especially useful in design and engineering tasks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Perimeter measures the total length of a shape’s boundary (like a fence), while area measures the surface coverage inside (like a carpet). One is length, the other is space!
Yes, absolutely – circumference is the perimeter of a circle, the total length of a curved boundary.
No, absolutely – it’s always zero or positive; length never goes minus.
Depends on the size of the shape: use a tape measure, rope, or measuring wheel – these are standard tricks when building fencing or tracks.
No, not an exact formula; For high accuracy, mathematical approximations (like Ramanujan’s) are used – a common practice in engineering.
Only linear: meters, cm, inches, feet – no length, square units!
Final Thoughts
Our Perimeter Calculator provides a fast, accurate, and user-friendly way to calculate the perimeter of virtually any geometric shape. With clear formulas, real-world examples, and built-in measurement guidance, it’s ideal for students, professionals, and everyday problem-solving.